Max’s Super Shred Protein - Summary: A Quick Preface
- Max's Super Shred is a protein supplement known for helping build "ripped, shredded muscle"
- Super Shred comes in a plastic tub containing 1.82kg of protein powder with two flavours: vanilla & chocolate
- The nutritional panel is comprehensive & detailed, showcasing seven complexes with 29 active ingredients
- The taste of Max's Super Shred is enjoyable, it mixes well with either a spoon, shaker, or blender
- Compared to other fat-burning proteins, Max's Super Shred contains a moderate amount of protein but has a wide variety of vitamins & minerals that some others do not
- Super Shred has a moderate proportion of protein at approximately 72%, lower carbohydrates, & low calories per serving, making it an excellent weight/fat loss protein
- Pros include the product's ergogenic potential, which positively affects weight loss, body composition, exercise performance, & recovery, as well as its substantial number of active ingredients
- Cons include the nutritional panel numbers not adding up perfectly
- Super Shred is recommended as a post-workout shake or a small snack for those seeking to lose weight & build lean muscle
- Recommendations include trying both flavours to avoid boredom & additionally including carbohydrates to restore glycogen levels after a workout
- Max's Super Shred is an easy-to-mix, great-tasting, & comprehensive protein supplement that can help with weight/fat loss and maintaining lean muscle
Max’s has carved itself a venerable reputation since its formation in 1989. Their large range of products and their well-recognised logo has over time gained almost a cult status within the bodybuilding community and almost anyone who trains frequently. Max’s Super Shred is by far one of their best-selling proteins due to its claim of being able to help build ‘ripped, shredded muscle’, something most bodybuilders or even the average trainer would seek to achieve. But does Max’s Super Shred formulation deserve its high standing?
Max’s Super Shred - First Impressions: What You Need to Know About the Packaging, Nutritional Panel, & Active Ingredients
Max’s Super Shred comes in a plastic tub containing 1.82kg (or 4lb) of protein of powder. On the front of the package is an impressive-looking picture of Max’s superhero mascot ‘Max’ along with several of the main claims of the product. The other panels include a large and extremely comprehensive nutritional panel, a sample diet plan with ‘getting ripped’ diet tips as well as an imposing, but extremely detailed explanation of all the primary active ingredients grouped into 7 complexes, each intended for a different ergogenic benefit. The powder is very fine in consistency with a subtle sweet smell. A 30g scoop is included in the product.
Max’s Super Shred - Taste and Mixability: Our Experience with the Vanilla & Chocolate Flavors
Max’s Super Shred comes in two different flavours: vanilla and chocolate. Both flavours are quite enjoyable when mixed as directed in 300 mL of liquid. Each flavour also has subtly sweet smells, none of which are overpowering. The beverages are not too sweet with no significant aftertaste or grittiness. However, when shaken, the mixture is quite foamy at the start, which may degrade the experience. As with most protein powders mixed with water, the viscosity of the end product is quite thin and while easily drinkable, is no match for a milk-based preparation. As the product is considered a fat-loss protein, the use of milk may be conflicting with overall weight loss goals, however, skim milk or unsweetened plant-based milk such as almond milk is an excellent choice to add not only some flavour but also extra protein. If you are on an extremely strict diet that avoids carbohydrates, then mixing with water is the best choice. Based on several reviews of the product, the flavour most preferred is chocolate.

The flavours of the Max’s Super Shred range of products mix very well with either a spoon, shaker or blender with no grittiness, clumps or residue when made as directed with 200mL of liquid. The preparation however does foam up with both the shaker and blender which settles within a few minutes.
Max’s Super Shred - Value: Is it Worth the Price?
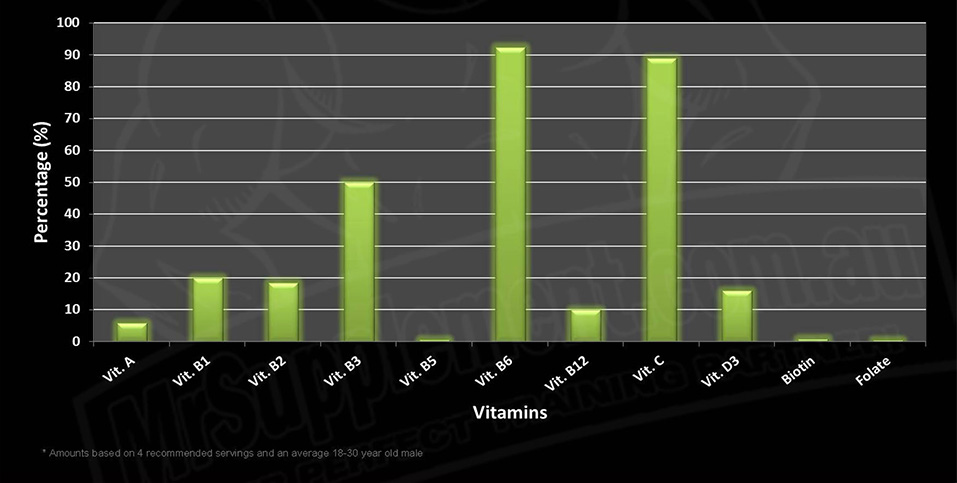
Max’s Super Shred comes in one size; 1.8kg and 2 official flavours. Compared to most other fat-burning proteins, Max’s contains only a moderate amount of protein on a gram-for-gram basis at 72% protein. It also contains a wide variety of vitamins and minerals, which proves to be an important factor as many people consider using this as a meal replacement and so it is essential that the necessary nutrition we are missing out from reducing food intake is met. Max’s Super Shred also has a substantial number of active ingredients to help with weight/fat loss while maintaining lean muscle, more so than many of its major competitors.
Size | Price/ g Protein ($) |
1.8kg | 0.05 |
Max’s Super Shred - Pros & Cons: A Comprehensive List of Benefits & Drawbacks
The Pros - With 7 complexes and 29 proposed active ingredients, Max’s Super Shred has left very little to chance in its ergogenic potential. In fact, the majority of the active ingredients have been shown in studies to positively affect weight loss, body composition, exercise performance and recovery. The inclusion of several active ingredients also increases the potential for synergistic effects which may have not been investigated in studies yet.
A high proportion of protein at approximately 72% along with lower carbohydrates and a low amount of calories per serving make Max’s Super Shred an excellent weight/fat loss protein. At 470 kJ, it is a third of the calories of a can of tuna but provides almost double the protein. In addition, one serving provides 13.1g of essential amino acids and 6.7g of branched-chain amino acids, more than enough to kickstart muscle protein synthesis mechanisms.
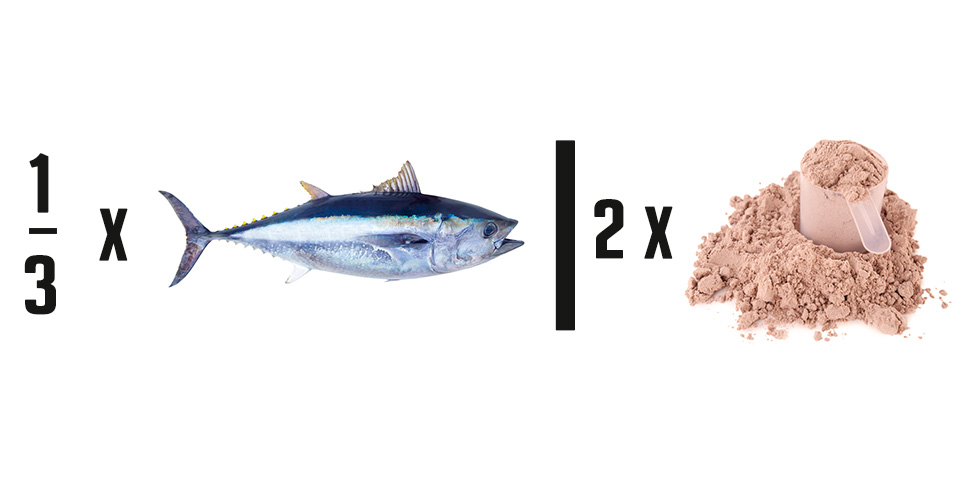
The Cons - While the nutrition panel is extremely comprehensive, unfortunately, a flaw within the packaging is that the numbers don’t seem to add up, which can create problems when comparing the amounts shown in the nutritional panel to ergogenic amounts used in studies. Also, because there are so many ingredients, it reduces the amount of each active ingredient per serve which can lower the effectiveness of each ingredient.
Some may think that the switch from a pure WPI powder to a blend containing WPI and calcium caseinate may be a step-down. However, using a slightly slower absorbing casein may actually improve the weight loss benefits of SuperShred. Slower digesting proteins can fuel muscles for a long and help to keep you fuller for extended periods, which are characteristics one would look for in a fat-loss shake.
Max’s Super Shred - Active Ingredients: What Makes it so Good
As Max’s Super Shred contains so many active ingredients, instead of listing them, this review will examine those active ingredients in their respective complex groups.
1. Carb Blocking Complex
The carb-blocking complex contains 4 active ingredients; phaseolamin, green coffee extract, hydroxy citric acid and chromium.
Ingredient | Function & Effectiveness |
Phaseolamin |
|
Green Coffee Extract (GCE) |
|
Hydroxy Citric Acid (HCA) |
|
Chromium |
|
2. Thermogenic Fat Incinerator Complex
The thermogenic fat incinerator complex contains 5 active ingredients; green tea, forskolin, guarana, carnitine, choline and inositol.
Ingredient | Function & Effectiveness |
Green Tea |
|
Forskolin |
|
Guarana |
|
Carnitine |
|
Choline & Inositol |
|
3. Appetite Modulation Complex
The appetite modulation complex contains 4 active ingredients; l-tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine and zinc.
Ingredient | Function & Effectiveness |
L-Tyrosine |
|
Tryptophan |
|
Phenylalanine |
|
Zinc |
|
4. Lean Muscle Growth Signalling Complex
The lean muscle growth signalling complex contains 5 active ingredients; l-leucine alpha-ketoglutarate, taurine, l-arginine alpha-ketoglutarate, magnesium and calcium.
Ingredient | Function and Effectiveness |
L-Leucine Alphaketoglutarate |
|
Taurine |
|
L-Arginine Alpha-ketoglutarate |
|
Magnesium |
|
Calcium |
|
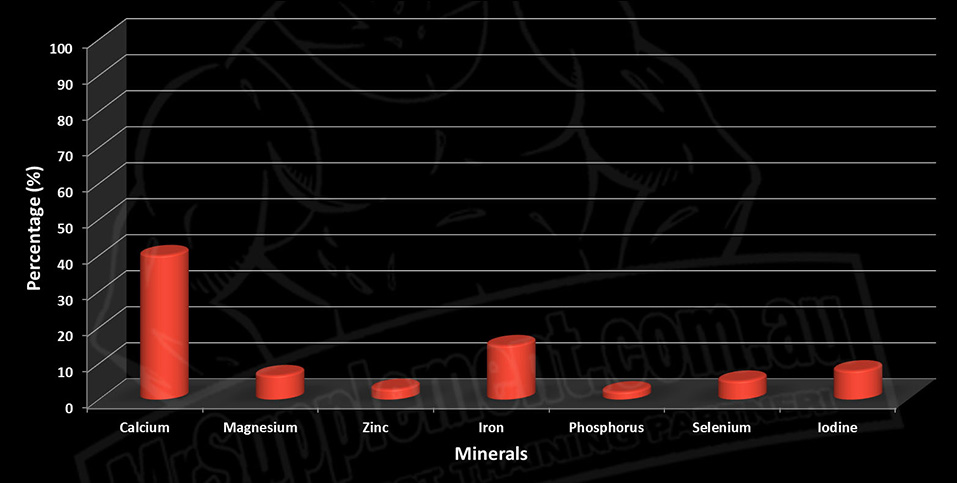
Max's Super Shred % of Mineral RDI's Met
5. Muscle Sparing Recovery Complex
The muscle-sparing recovery complex contains 3 active ingredients; l-glutamine, glutamine peptides and branched chains of amino acids.
Ingredient | Function and Effectiveness |
L-Glutamine |
|
Glutamine Peptides |
|
Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) |
|
6. Cortisol Regulating Complex
The cortisol-regulating complex contains 2 active ingredients; phosphatidylserine and l-theanine.
Ingredient | Function and Effectiveness |
Phosphatidylserine |
|
L-Theanine |
|
7. Bio-Engineered Protein Complex
The bio-engineered protein complex contains 2 active ingredients; high glycomacropeptide whey protein isolate and high beta whey fraction whey protein isolate.
Ingredient | Function and Effectiveness |
High Glycomacropeptide Whey Protein Isolate |
|
High Beta Whey Fraction Whey Protein |
|
Max’s Super Shred - Conclusion: Our Final Thoughts on this Protein Powder
Conclusion: Overall, Max’s Super Shred is a great-tasting and easy-to-mix weight/fat loss protein, which can be consumed as either a post-workout shake or a small snack. As weight loss takes time, recommendations are to consider obtaining all three flavours to avoid boredom, which can affect compliance. Including carbohydrates may be beneficial in helping to restore glycogen levels after a strenuous workout. With a renowned reputation, Max’s has created a comprehensive formulation with a wide variety of active compounds, vitamins, minerals and an exceptionally high amount of protein per serve.
References
-
1 Barrett ML, Udani JK. ‘A proprietary alpha-amylase inhibitor from white bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): a review of clinical studies on weight loss and glycemic control.’ Nutr J. 2011 Mar 17;10:24.
2 Onakpoya I, Terry R, Ernst E. ‘The use of green coffee extract as a weight loss supplement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials.’ Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2011;2011. pii: 382852. Epub 2010 Aug 31.
3 Preuss HG, Rao CV, Garis R, Bramble JD, Ohia SE, Bagchi M, Bagchi D. ‘An overview of the safety and efficacy of a novel, natural(-)-hydroxycitric acid extract (HCA-SX) for weight management.’ J Med. 2004;35(1-6):33-48.
4 Pittler MH et al. ‘Chromium picolinate for reducing body weight: Meta-analysis of randomized trials.’ International Journal of Obesity (2003) 27, 522–529. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802262
5 Dulloo AG, Duret C, Rohrer D, Girardier L, Mensi N, Fathi M, Chantre P, Vandermander J. ‘Efficacy of a green tea extract rich in catechin polyphenols and caffeine in increasing 24-h energy expenditure and fat oxidation in humans.’ Am J Clin Nutr. 1999 Dec;70(6):1040-5.
6 Henderson S, Magu B, Rasmussen C, Lancaster S, Kerksick C, Smith P, Melton C, Cowan P, Greenwood M, Earnest C, Almada A, Milnor P, Magrans T, Bowden R, Ounpraseuth S, Thomas A, Kreider RB. ‘Effects of coleus forskohlii supplementation on body composition and hematological profiles in mildly overweight women.’ J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2005 Dec 9;2:54-62.
7 Anderson T, Foght J (2001). "Weight loss and delayed gastric emptying following a South American herbal preparation in overweight patients". J Hum Nutr Diet 14 (3): 243.
8 Wutzke KD, Lorenz H. ‘The effect of l-carnitine on fat oxidation, protein turnover, and body composition in slightly overweight subjects.’ Metabolism. 2004 Aug;53(8):1002-6.
9 EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to choline and contribution to normal lipid metabolism (ID 3186), maintenance of normal liver function (ID 1501), contribution to normal homocysteine metabolism (ID 3090), maintenance of normal neurological function (ID 1502), contribution to normal cognitive function (ID 1502), and brain and neurological development (ID 1503) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA Journal 2011;9(4):2056. [23 pp.]. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2056.
10 Giordano D, Corrado F, Santamaria A, Quattrone S, Pintaudi B, Di Benedetto A, D'Anna R. ‘Effects of myo-inositol supplementation in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome: a perspective, randomized, placebo-controlled study.’ Menopause. 2011 Jan;18(1):102-4.
11 Hao S, Avraham Y, Bonne O, Berry EM (2001). "Separation-induced body weight loss, impairment in alternation behavior, and autonomic tone: effects of tyrosine". Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 68 (2): 273–81. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(00)00448-2. PMID 11267632
12 Oldman AD et al. ‘Effect of acute tryptophan depletion on mood and appetite in healthy female volunteers.’ J Psychopharmacol. Jan. 1994:8 (1): 8-13
13 Ballinger AB, Clark ML. ‘L-phenylalanine releases cholecystokinin (CCK) and is associated with reduced food intake in humans: evidence for a physiological role of CCK in control of eating.’ Metabolism. 1994 Jun;43(6):735-8.
14 Chen MD, Song YM, Lin PY. ‘Zinc may be a mediator of leptin production in humans.’ Life Sci. 2000 Apr 21;66(22):2143-9.
15 Koopman R, Wagenmakers AJ, Manders RJ, Zorenc AH, Senden JM, Gorselink M, Keizer HA, van Loon LJ. ‘Combined ingestion of protein and free leucine with carbohydrate increases postexercise muscle protein synthesis in vivo in male subjects.’ Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Apr;288(4):E645-53. Epub 2004 Nov 23.
16 Warskulat, U. Flogel, C. Jacoby, H.-G. Hartwig, M. Thewissen, M. W. Merx, A. Molojavyi, B. Heller-Stilb, J. Schrader and D. Haussinger (2004). "Taurine transporter knockout depletes muscle taurine levels and results in severe skeletal muscle impairment but leaves cardiac function uncompromised". The FASEB Journal 18 (3): 03–0496fje. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0496fje. PMID 14734644
17 Zhang, M; Bi, LF; Fang, JH; Su, XL; Da, GL; Kuwamori, T; Kagamimori, S (2004). "Beneficial effects of taurine on serum lipids in overweight or obese non-diabetic subjects". Amino Acids 26 (3): 267–71. doi:10.1007/s00726-003-0059-z. PMID 15221507.
18 Besset A, Bonardet A, Rondouin G, Descomps B, Passouant P. Increase in sleep related GH and Prl secretion after chronic arginine aspartate administration in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1982;99(1):18-23.
19 Bohl CH, Volpe SL. ‘Magnesium and exercise.’ Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2002;42(6):533-63.
20 Kreider RB et al. ‘ISSN exercise & sport nutrition review: research & recommendations.’ J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010; 7: 7.
21 Adibi SA. ‘Intestinal phase of protein assimilation in man.’ Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Feb;29(2):205-15.
22 Candeloro N, Bertini I, Melchiorri G, De Lorenzo A. ‘Effects of prolonged administration of branched-chain amino acids on body composition and physical fitness.’ Minerva Endocrinol. 1995 Dec;20(4):217-23.
23 Kingsley MI, Wadsworth D, Kilduff LP, McEneny J, Benton D. ‘Effects of phosphatidylserine on oxidative stress following intermittent running.’ Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005 Aug;37(8):1300-6.
24 Starks MA, Starks SL, Kingsley M, Purpura M, Jäger R. ‘The effects of phosphatidylserine on endocrine response to moderate intensity exercise.’ J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Jul 28;5:11.
25 Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja L, Ohira H (2007). "L-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses". Biol Psychol 74 (1): 39–45.
26 Burton-Freeman BM. ‘Glycomacropeptide (GMP) is not critical to whey-induced satiety, but may have a unique role in energy intake regulation through cholecystokinin (CCK).’ Physiol Behav. 2008 Jan 28;93(1-2):379-87. Epub 2007 Oct 26.

