Creatine for Power, Energy & Muscle Gain
- 99.9% Pure Free Form Creatine Monohydrate
- Boost Athletic Performance
- Build Extra Lean Muscle & Improve Physique
- Improve Strength & Power for High Intensity Exercise

Musashi Creatine Monohydrate is a dietary precursor of creatine phosphate (phosphocreatine). Creatine phosphate is the carrier that replenishes levels of ATP in muscle cells when stores have been depleted during power exercise. Supplementation of creatine in higher doses will also provide energy for muscle cells during periods of growth - a process called the phosphocreatine energy shuttle. Creatine monohydrate supplementation can not only boost athletic performance but also encourage the body to lay down extra lean muscle, improving the physique.
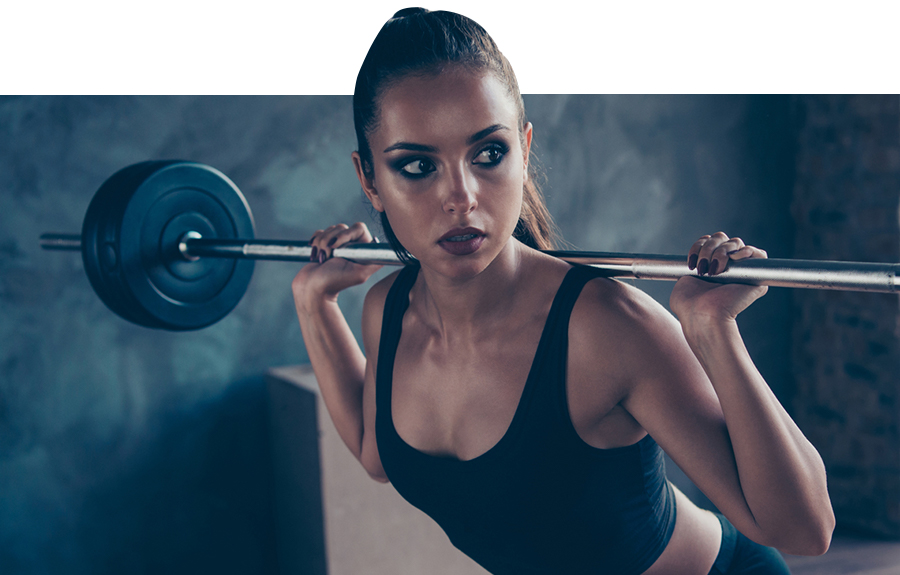

Musashi Creatine: Key Benefits
- Pure free-form powder
- Energy for muscle growth
- Precursor of Creatine Phosphate
- Improves high-intensity exercise performance
- Easy mixing (micronised creatine)
Musashi Creatine
- Is Creatine Safe?
Yes, Creatine is a natural amino acid present in the body of humans and animals. The human body has 100-115 grams of creatine in the form of creatine phosphate. No negative side effects have been noted in the research with the recommended levels of supplementation.
- Are there any noted side effects?
Creatine is so efficient at shuttling water into the intramuscular compartment, that an emergent side effect associated with it is that of muscle cramping. This most often occurs when too little fluid is consumed whilst supplementing with creatine. Muscle Cramping, strains and tears are all anecdotal evidence that are not supported by scientific fact. Creatine draws water away from the internal working organs and therefore if you take a lot with no water then a mild stomach cramp will occur.
- Is Creatine safe to take for long periods?
In truth nobody knows although it does appear to be safe with no adverse effects reported in any study which we are aware of. Some people have been taking as much as 20-30 grams a day since it was first available in 1990.
- What is Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP)?
ATP is the organic compound found in muscle which, upon being broken down enzymatically, yields energy for muscle contraction. Creatine enhances your body's ability to make protein within the muscle fibres, which also increases your muscle mass (Creatine increases cellular hydration. The hydrated muscle has increased permeability, which allows more amino acids into the muscle cell). Building up a supply of these contractile proteins ( actin and myosin ) increases your muscles ability to perform physical work. The bottom line here, is that creatine will allow you to to perform more repetitions with a given weight. This will increase the time under tension, thus increasing the recruitment of muscle fibres, which will in turn increase the number of fibres stimulated. It also prevents your body from relying on another energy system called glycolysis, which has lactic acid as a byproduct. Lactic acid creates the burning sensation you feel during intense exercise.

Taste: Not bad but not good either, mix it with milk to improve, or rather get rid of, the taste.
Solubility: Not very good, but that is the case for almost all creatine monohydrate supplements. Small serving sizes mean this isn’t a great concern (unless you’re doing creatine loading and need to take up to 20g, then it may be a bigger issue).
Side Effects: Nil adverse side effects were experienced whilst taking this product.
Cost Effectiveness: Serving size is 5g so that equates to about 100 serves per 500g tub. Cost effectiveness is OK. Depending on whether you do creatine loading or not, then cost effectiveness is not great.
Conclusion: A good and effective creatine mono-hydrate product; however there are more cost effective creatine supplements out there.